Lipedema Causes: Genetics and Lifestyle Impact
Key Takeaways
-
Recognize Symptoms Early: Early identification of lipedema symptoms, such as disproportionate fat distribution in the legs and arms, primary lipodystrophy, and pathological lipid profiles in adipose tissue, can lead to better management and treatment outcomes, including liposuction.
-
Genetics Play a Role: Genetic predisposition is a significant factor in developing lipedema and fat accumulation increase, so understanding your family history can be crucial.
-
Hormonal Changes Matter: Hormonal influences, especially during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can trigger or worsen lipedema, sometimes necessitating liposuction to remove excess fat.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments Help: Adopting a healthier lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can mitigate some symptoms of lipedema and improve overall well-being alongside lipedema treatments like liposuction.
-
Accurate Diagnosis is Key: Differentiating between lipedema and conditions like lymphoedema is essential for proper treatment; consult specialists for accurate diagnosis and consider liposuction.
-
Seek Support Networks: Joining support groups or finding communities of individuals with lipedema can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Understanding Lipedema
Chronic Condition
Lipedema is a chronic condition. It causes abnormal accumulation of fat in specific parts of the body, requiring lipedema treatments. This condition mainly affects the legs and arms. The fat deposits are often painful and tender.
Distinct Medical Condition
Recognizing lipedema as a distinct medical condition is crucial. It is different from obesity or lymphedema. Obesity involves general fat accumulation across the body, while lipedema targets specific areas. Lymphedema involves fluid buildup, not fat.
Primarily Affects Women
Lipedema primarily affects women. It usually starts around puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. These hormonal changes trigger the condition. Men can get lipedema, but it is rare.
Early Stage Lipedema Treatment
Early stage lipedema treatment can help manage symptoms. Treatments include compression garments, manual lymphatic drainage, and exercise. These treatments aim to reduce pain and improve mobility.
Fat Tissue Involvement
Lipedema involves subcutaneous fat tissue. This is the layer of fat just under the skin involved in lipedema treatments. The fat cells in this layer become enlarged and multiply abnormally, necessitating lipedema treatments. This leads to the characteristic swelling seen in lipedema.
Emotional Impact
The emotional impact of lipedema can be severe. Many women feel frustrated due to misdiagnosis or lack of support. Joining a lipedema support group can provide emotional relief and community support.
Advanced Lipedema
Advanced lipedema can lead to more severe symptoms. These include extreme pain, limited mobility, and joint issues. At this stage, surgical options like liposuction may be considered.
Research and Support
Organizations like the Lipedema Foundation are vital for research and support. They fund studies to understand lipedema better and develop new treatments. They also provide resources for patients and healthcare providers.
Identifying Symptoms
Common Signs
Lipedema presents with several distinct symptoms. One of the most common signs is painful, swollen limbs. This swelling is due to an abnormal accumulation of fat in the legs and arms. People with lipedema often notice that their lower body is disproportionately larger than their upper body.
Another key symptom is the presence of fatty deposits. These deposits are usually found in the legs and sometimes in the arms. The skin over these areas may feel soft and doughy. Bruising easily in these regions can also occur.
Symmetrical Fat Distribution
A unique characteristic of lipedema is its symmetrical nature. The fat tends to be evenly distributed on both sides of the body. This symmetry helps differentiate lipedema from other conditions like simple obesity, where fat distribution can be more random.
Diet and exercise do not typically improve lipedema. Patients often find that no matter how much they diet or exercise, the affected areas remain unchanged. This lack of response to lifestyle changes can be frustrating and disheartening.
Hormonal Influence
Hormonal changes play a significant role in the progression of lipedema. Symptoms often worsen during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. These periods involve significant hormonal shifts that can exacerbate the condition.
For instance, many women first notice symptoms during puberty. Others may experience a worsening of symptoms during pregnancy when hormonal levels fluctuate significantly. Menopause is another critical time when symptoms can intensify.
Skin Changes
The skin over lipedema-affected areas can undergo specific changes. It may become tender and sensitive to touch. Some people report feeling a heavy or aching sensation in the affected limbs.
Skin texture can also change, becoming more prone to developing cellulite-like dimples. In advanced cases, the skin might develop large folds due to excessive fat deposits.
Emotional Impact
Living with lipedema can have an emotional toll. The visible changes in body shape and size can affect self-esteem and body image. Many individuals feel self-conscious about their appearance.
The pain and discomfort associated with lipedema can limit daily activities. This limitation can lead to feelings of frustration and helplessness.
Exploring Causes
Genetic Factors
The exact causes of lipedema remain unknown. However, genetic factors are believed to play a significant role. Many cases show a family history of the condition. This suggests that certain genes could increase the risk of developing lipedema. Research indicates that up to 60% of those with lipedema have a relative with the same condition.
Hormonal Influence
Female hormones may also contribute to the development of lipedema. The condition primarily affects women and often starts or worsens at times of hormonal change. These times include puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. This pattern points to estrogen as a potential factor in lipedema’s onset and progression.
Not Linked to Obesity
Lipedema can affect individuals of all body weights. It is not solely linked to obesity. People with normal weight can develop lipedema just as those who are overweight or obese can. This distinction is important because it highlights that lipedema is a distinct medical condition, not simply a result of excess body fat.
Impact on the Body
Lipedema results in the abnormal distribution of fat cells in the body. These fat cells often accumulate in the legs and arms but spare the feet and hands. The affected areas become larger and more painful over time. Unlike regular fat, lipedemic fat is resistant to diet and exercise.
Psychological Effects
The physical changes caused by lipedema can lead to emotional distress. Those affected may feel self-conscious about their appearance. They might also face misunderstandings from others who mistake their condition for simple obesity. This misperception can result in social stigma and reduced self-esteem.
Other Contributing Factors
Other factors might contribute to the development of lipedema, though they are less understood. Inflammation and vascular issues could play a role. Some studies suggest that blood vessels in lipedemic tissue might be weaker or more prone to leaking fluid, leading to swelling and pain.
Real-Life Example
Consider Sarah, a woman diagnosed with lipedema at age 30 after years of unexplained weight gain in her legs despite maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Her mother and grandmother had similar symptoms but were never diagnosed. Sarah’s case highlights both the genetic link and the importance of awareness about this condition.
Genetic and Hormonal Influences
Genetic Factors
Lipedema often runs in families. If female relatives have lipedema, the risk increases. Studies show a genetic link to the condition. This suggests that certain genes may influence fat distribution and accumulation.
Research indicates that lipedema is more common in females. The condition rarely affects males. This points to a strong genetic component tied to sex chromosomes.
Hormonal Shifts
Hormonal changes can trigger lipedema. Puberty, pregnancy, and menopause are key times for onset and progression. During puberty, hormonal surges can cause pathological adipogenesis, leading to abnormal fat accumulation.
Pregnancy involves significant hormonal shifts. These changes can worsen or trigger lipedema symptoms. Women may notice increased fat accumulation during this time.
Menopause also brings hormonal changes. Decreased estrogen levels can affect fat distribution. This shift can lead to the progression of lipedema in middle-aged women.
Hormonal Imbalances
Research suggests a link between lipedema and hormonal imbalances. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) involve hormonal disruptions. These conditions may increase the risk of developing lipedema.
Hormones regulate many body processes, including fat storage and distribution. Imbalances in these hormones can contribute to lipedema development. For example, insulin resistance, often seen in PCOS, can affect how the body stores fat.
Fat Distribution Patterns
Lipedema affects body fat distribution uniquely. It typically causes disproportionate fat buildup in the legs and arms, sparing the hands and feet. This pattern is different from general obesity.
The fat tissue in lipedema is different from regular body fat. It may feel nodular or lumpy under the skin. This distinct characteristic helps differentiate it from other conditions.
Female Predominance
Most people with lipedema are female. This predominance highlights the role of female hormones in the condition’s development. Estrogen and progesterone play significant roles in regulating body fat.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Diet Impact
Diet plays a significant role in managing lipedema symptoms. People with lipedema often have excess fat buildup, particularly in the legs and arms. A balanced diet can help manage this condition. Health professionals recommend diets low in processed foods and sugars. These foods can contribute to inflammation and worsen symptoms.
A diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is beneficial. Avoiding high-sodium foods can also reduce swelling. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps as well.
Exercise Benefits
Exercise is crucial for managing lipedema. Regular physical activity can help reduce fatty deposits and improve overall health. Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, and cycling are recommended. These activities are gentle on the joints and can aid in reducing pain and swelling.
Strength training can also be beneficial. It helps build muscle mass and improve circulation. This can alleviate some symptoms of lipedema.
Obesity Risk
Obesity is a risk factor for worsening lipedema symptoms. Excess weight can put additional stress on the body, exacerbating the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is important. People with morbid obesity may experience more severe symptoms.
Health professionals often work with patients to create personalized weight management plans. These plans include dietary changes and exercise routines tailored to individual needs.
Environmental Influence
Environmental factors do not directly cause lipedema. However, they can influence symptom severity. Exposure to certain materials or conditions might aggravate symptoms. For example, extreme heat or cold can affect blood flow and swelling.
Living areas with limited access to healthy foods or safe places to exercise can also impact symptom management. Creating a supportive environment is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Family History
Family history plays a role in the development of lipedema. While environmental factors influence symptom management, genetics largely determine the condition’s onset. If a person has a family history of lipedema, they should be aware of their lifestyle choices.
Healthy habits can potentially mitigate the progression of symptoms even if the condition is genetically predisposed.
Diagnosing Correctly
Diagnostic Challenges
Lipedema is often mistaken for other conditions. Obesity and lymphedema share similar symptoms. This makes diagnosis difficult. Doctors may confuse lipedema with these conditions. Misdiagnosis can delay proper treatment.
Diagnostic Criteria
Specific criteria help diagnose lipedema. Fat deposits appear in the lower body. These deposits are symmetrical. They do not affect the feet. Pain is another key symptom. Patients often feel tenderness in affected areas. Bruising occurs easily due to fragile blood vessels.
Differential Diagnosis
Doctors must rule out other conditions. Obesity involves general weight gain, not localized fat deposits. Lymphedema causes swelling that affects the feet and hands, unlike lipedema. A thorough examination helps differentiate these conditions.
Importance of Expertise
Seek a diagnosis from a knowledgeable healthcare professional. Not all doctors are familiar with lipedema. Specialists understand the nuances of this condition. They use specific tools and tests to confirm a diagnosis.
Lipedema vs Lymphoedema Differences
Fat Accumulation vs Fluid Buildup
Lipedema and lymphoedema are different conditions. Lipedema is marked by fat tissue changes. These changes lead to the buildup of fatty tissue. In contrast, lymphoedema involves fluid accumulation in the tissues.
Symmetrical vs Unilateral Impact
Lipedema usually affects both limbs symmetrically. This means both legs or arms show similar signs. Lymphoedema can be unilateral, affecting just one limb. This difference helps in diagnosing these conditions correctly.
Diagnosis Importance
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatments. Knowing whether a patient has lipedema or lymphoedema guides the right therapy approach.
Treatment Approaches
Lipedema Treatments
Lipedema treatments focus on reducing fat tissue. Some common methods include:
-
Compression garments
-
Manual lymphatic drainage
-
Lipectomy and liposuction
These methods help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lymphoedema Treatments
Lymphoedema treatments aim at reducing fluid buildup. Common therapies include:
-
Compression bandaging
-
Manual lymph drainage
-
Exercise programs
These treatments help control swelling and improve limb function.
Importance of Specialized Care
Both conditions require specialized care. Lipedema patients may need different approaches than those with lymphoedema. Accurate diagnosis ensures that patients receive the most effective treatment.
Treatment Overview
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is a common treatment for lipedema. It involves wearing compression garments to improve blood and lymph flow. These garments help reduce swelling and discomfort in the affected tissues. They should be worn daily for best results.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a specialized massage technique. It helps move excess lymph fluid out of swollen areas. MLD can provide relief from pain and heaviness. It is often performed by trained therapists.
Surgical Options
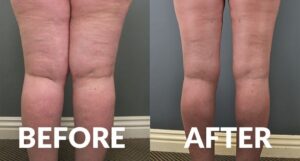
In some cases, surgery may be considered. Liposuction is a surgical option to remove excess fat tissue. This procedure can improve mobility and reduce pain. However, it is not a cure and symptoms may return over time.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing lipedema symptoms. A healthy diet can help control weight and reduce inflammation. Regular exercise improves overall health and reduces stress on the body.
Focus on Symptom Management
There is currently no cure for lipedema. Treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Symptom management includes reducing pain, improving mobility, and preventing complications.
Finding Support
Healthcare professionals
Seeking support from healthcare professionals is crucial. They can provide expert advice and treatment plans. Look for doctors who specialize in lipedema. These specialists understand the condition better than general practitioners.
Consultations with these experts can make a big difference. They can offer personalized care. Compression garments and other treatments may be recommended. Regular check-ups ensure that the treatment plan is working.
Support groups
Joining lipedema support groups can be beneficial. These groups offer emotional and practical support. Members share their experiences and advice.
Online communities are also helpful. Websites dedicated to lipedema often have forums and discussion pages. Connecting with others who have the same condition provides comfort and understanding.
Education and advocacy
Education about lipedema is essential. The more you know, the better you can manage the condition. Read articles, watch videos, and attend seminars on lipedema.
Advocacy is also important. Raising awareness helps others understand what you are going through. It can lead to better services and support for everyone affected by lipedema.
Closing Thoughts
Understanding lipedema is crucial for managing this often misunderstood condition. Identifying the symptoms, exploring causes, and distinguishing it from similar disorders can empower you to seek accurate diagnoses and effective treatments. Genetic, hormonal, environmental, and lifestyle factors all play a role, emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive approach to care.
Don’t navigate this journey alone. Seek support from medical professionals and communities who understand your struggles. Stay informed, advocate for yourself, and explore treatment options that work best for you. Your proactive steps can make a significant difference. Ready to take control of your health? Start today—reach out for support and stay connected with reliable resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is lipedema?
Lipedema is a chronic condition causing an abnormal buildup of fat, primarily in the legs and arms. It often leads to pain and mobility issues.
What are the main causes of lipedema?
The exact cause of lipedema is unknown. However, genetic and hormonal factors play significant roles. Environmental and lifestyle factors may also contribute.
How can I identify symptoms of lipedema?
Common symptoms include disproportionate fat accumulation in the lower body, pain, easy bruising, and swelling that doesn’t respond to diet or exercise.
Are genetic factors involved in lipedema?
Yes, genetics significantly influence lipedema. It often runs in families, suggesting a hereditary component.
Can lifestyle changes help manage lipedema?
While lifestyle changes alone can’t cure lipedema, maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
How is lipedema different from lymphoedema?
Lipedema primarily affects fat tissue and usually starts at puberty or menopause. Lymphoedema involves swelling due to lymphatic fluid buildup and can occur at any age.
What treatments are available for lipedema?
Treatments include compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, physical therapy, and in severe cases, liposuction. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized options.

 /
/ 