Fat Grafting Techniques: Innovations and Applications in Aesthetics

Fat grafting techniques, utilizing mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have transformed the world of cosmetic procedures in society. Unlike traditional methods that rely on implants, fat grafting uses your own body fat and mscs for a more natural look. This fat grafting procedure offers benefits like reduced scarring and a lower risk of complications, enhancing autologous fat grafting outcomes through effective fat graft harvesting.
Patients can achieve fuller lips, enhanced cheeks, and smoother skin with fat grafting outcomes without the need for synthetic materials. The process of neck fat grafting is simple yet effective, making it a popular choice among those seeking subtle enhancements. Whether you want to rejuvenate your appearance or restore lost volume, fat grafting could be the answer. Discover how these innovative techniques, including fat graft, can help you achieve your aesthetic goals while ensuring safety and satisfaction.
Key Takeaways
- Fat grafting is a versatile technique that can enhance various areas of the body, so consider it for both cosmetic and reconstructive purposes.
- Understanding different fat harvesting techniques is crucial; choose the method that best suits your needs for optimal results.
- Proper processing methods can significantly affect the quality of the graft, ensuring better survival rates of the fat cells.
- Preparing the recipient site for fat graft carefully can lead to more successful outcomes, so follow recommended practices closely.
- Common areas for fat grafting include the face, breasts, and hands; evaluate these options based on your aesthetic goals.
- Postoperative care, especially after a fat graft, is essential for recovery; adhere to guidelines provided by your healthcare provider to minimize complications.
Understanding Fat Grafting
Definition
Fat grafting is a cosmetic and reconstructive procedure. It involves transferring fat from one area of the body to another. This technique uses the patient’s own tissue, making it an autologous fat graft. The process provides a natural solution for enhancing volume and contour using fat graft.
Purpose
The main purpose of fat grafting is twofold. First, it enhances volume in areas like the face or breasts through fat graft. Second, it helps in contouring the body. Patients choose this method for its ability to create a more youthful appearance with fat grafts without synthetic fillers.
Techniques
Several techniques exist for fat grafting. Basic fat grafting includes harvesting, processing, and injecting fat. The fat grafting process begins with liposuction to collect fat from areas like the abdomen or thighs. After collection, the fat undergoes processing. This step removes impurities and prepares it for injection.
Popularity
Fat grafting has gained popularity in recent years. Advancements in technique have improved safety and effectiveness. Many patients prefer this fat graft method over synthetic options due to its natural results. Research shows that fat graft take rates are increasing with better processing methods.
Applications
Fat grafting serves various applications. Facial fat grafting helps restore volume lost due to aging. It can fill hollows under the eyes with fat graft or enhance cheekbones. In breast reconstruction, fat grafting offers a way to restore shape after surgery or trauma. Large volume fat grafting can also address significant deformities.
Outcomes
The outcomes of fat grafting can be very positive. Patients often report satisfaction with their new appearance. Studies show that fat graft vascularization plays a key role in success. Proper blood supply ensures the longevity of the transferred fat.
Research
Ongoing research focuses on improving fat graft processing methods. Scientists study ways to enhance fat graft storage and increase viability. Innovations aim to boost fat graft outcomes and reduce complications.
Considerations
Patients should consider several factors before undergoing fat grafting procedures. Potential risks include infection or uneven results. Discussing these fat graft options with a qualified surgeon is essential for informed decision-making.
Fat Harvesting Techniques
Liposuction Use
Liposuction is the primary method for fat extraction. This procedure removes fat from donor areas like the abdomen, thighs, or flanks. Surgeons use a cannula, which is a thin tube, to suction out unwanted fat.
The process begins with fat graft markings on the skin to identify target areas. Next, the surgeon injects tumescent fluid into these areas. This fluid contains a local anesthetic and epinephrine. It helps reduce bleeding and makes fat removal easier.
Cannula Importance
Using thin cannulas is crucial in the fat harvesting process. These small tubes minimize damage to the fat cells during extraction. Less damage means more viable fat can be transferred later.
Surgeons prefer to use cannulas that are 3 mm or smaller. This size allows for precise movements within the tissue. As a result, it reduces trauma to surrounding tissues and improves overall outcomes.
Tumescent Fluid Role
Tumescent fluid plays a significant role in liposuction procedures. It helps create space in the fatty tissue, making it easier to extract fat. The fluid also reduces blood loss during surgery.
By minimizing bleeding, tumescent fluid enhances patient safety. Patients experience less bruising and swelling post-operation. This leads to quicker recovery times and better results for fat transfer patients.
Fat Processing Techniques
After harvesting, the next step involves fat processing techniques. This ensures that only healthy fat cells remain for transfer. Surgeons often use methods like centrifugation or filtration.
Centrifugation spins the harvested fat at high speeds. This separates unwanted fluids and damaged cells from healthy fat cells. Filtration involves passing fat through a fine mesh to remove impurities.
Both methods improve fat transfer viability, ensuring high survival rates for injected fat. Healthy fat cells lead to better aesthetic results after grafting.
Fat Transfer Methods
Fat can be transferred using various techniques after processing. Surgeons inject it into targeted areas such as the face, breasts, or buttocks. The injection technique matters greatly for successful integration of the fat.
Surgeons often use a microcannula for injections. These small tubes allow for precise placement of fat cells in specific layers of tissue. Proper placement promotes better blood supply and enhances survival rates of the grafted fat.
Processing Methods
Decanting Process
Decanting plays a crucial role in fat grafting. This process separates fat from excess fluids and impurities after extraction. Surgeons collect the harvested fat into a container. They allow it to sit for some time. During this period, the heavier fluids settle at the bottom. The lighter fat rises to the top.
Once settled, surgeons carefully pour off the top layer of fat. This leaves behind unwanted fluids and debris. The result is cleaner fat that is ready for further processing. This method is simple but effective. It helps maintain the quality of the fat tissue.
Centrifugation Technique
Centrifugation is another important method in fat processing. It uses rapid spinning to enhance separation. Surgeons place the collected fat into a centrifuge machine. This machine spins at high speeds. The centrifugal force causes denser materials to move outward.
As a result, impurities and excess fluids are separated from the fat cells. Centrifugation provides several benefits. It purifies and concentrates fat cells, leading to better graft survival rates. Studies show that centrifuged fat has higher viability compared to non-centrifuged samples. This technique ensures that more healthy cells are available for reinjection.
Filtration Method
Filtration serves as an alternative to both decanting and centrifugation. This method involves passing harvested fat through a filter system. The filter traps larger particles while allowing smaller fat cells to pass through.
Surgeons can use filters with various pore sizes depending on their needs. This flexibility allows for customization based on specific conditions or areas being treated. Filtration can reduce trauma to the fat cells during preparation, which helps retain their integrity.
Both centrifugation and filtration methods offer distinct advantages. They ensure that only quality fat tissues are used in grafting procedures.
Applications and Areas
Fat grafting techniques have various applications in medical fields. These include reconstructive surgery and cosmetic enhancements. Surgeons often target areas such as the face, hands, and even bone defects.
In facial rejuvenation, grafting adds volume and smooths out wrinkles. In hand surgeries, it restores lost volume due to aging or injury. Bone areas may benefit from grafting as well, especially in reconstructive procedures.
The choice of processing technique depends on the desired outcome and patient conditions.
Preparing the Recipient Site
Importance of Environment
Creating a suitable environment in the recipient area is crucial. Optimal fat cell survival depends on proper preparation. The recipient site must be clean and free from infection. This helps prevent complications during recovery. Surgeons often use sterile techniques to ensure safety.
The donor site also plays a vital role. Fat is usually harvested from areas like the abdomen or thighs. The quality of the fat affects its viability in the new location. It’s essential to choose a healthy donor site for the best results.
Tunneling Technique
Surgeons utilize tunneling techniques to distribute fat evenly in the recipient area. This method involves creating small tunnels within the tissue. It allows the fat to spread out instead of clumping together. Even distribution leads to smoother results.
Tunneling reduces the risk of lumps forming under the skin. Uneven fat placement can lead to unsatisfactory outcomes. By using this technique, surgeons improve overall aesthetics. A well-prepared recipient site enhances the final appearance.
Planning for Natural Results
Careful planning is necessary for achieving natural-looking results. Surgeons assess the recipient area before starting the procedure. They consider factors like skin texture and existing contours. This assessment helps in deciding how much fat to inject and where.
A detailed plan allows for adjustments during surgery. Surgeons can adapt based on real-time observations. This flexibility contributes to better outcomes.
Years of experience play a significant role here. Skilled surgeons understand how different techniques affect results. They know which areas require more attention and care.
Techniques Employed
Several specific techniques enhance fat grafting success:
- Layering: Injecting fat in layers helps maintain volume.
- Micro-fat grafting: Smaller fat particles allow for better integration into the surrounding tissue.
- Pressure control: Applying appropriate pressure during injection prevents damage.
These methods help create a more natural look and feel after surgery.
Post-Procedure Care
Post-operative care is also essential for success. Patients need guidance on how to care for their new contours. Following instructions about physical activity and compression garments aids healing.
Monitoring the recipient site closely helps identify potential issues early on. Early intervention can prevent complications from arising.
Common Areas for Fat Grafting
Facial Applications
Facial fat grafting is a popular method. It helps restore youthful contours and volume. Patients often seek this treatment to fill in areas like the cheeks and under the eyes. This technique can smooth out wrinkles and enhance facial features.
The process involves removing fat from a donor area, typically using modern liposuction methods. After harvesting, the fat is purified and injected into specific areas of the face. Many patients notice an immediate improvement in their appearance. Over time, the results can become even more natural as the body integrates the fat.
Breast Grafting
Fat grafting also plays a significant role in breast procedures. It is commonly used for both breast reconstruction and augmentation. For breast reconstruction, doctors use fat grafting to restore volume after mastectomy or injury. This technique provides a more natural look compared to implants.
In augmentation cases, patients may choose fat grafting to enhance breast size without implants. The procedure offers a dual benefit: reducing unwanted fat from other areas while enhancing breast volume. Many women appreciate the subtlety of this approach.
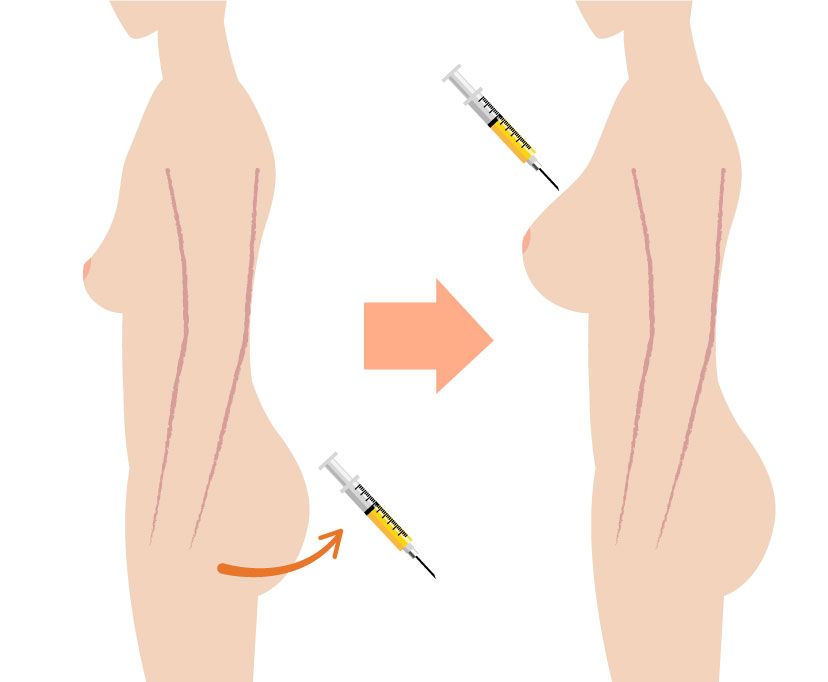
Buttocks Enhancement
Another common fat grafting application is buttocks enhancement. Known as Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL), this procedure has gained immense popularity in recent years. Patients prefer this method because it uses their own fat instead of synthetic materials.
Surgeons harvest fat from areas like the abdomen or thighs. They then inject it into the buttocks to create a fuller and rounder shape. This method not only enhances the buttocks but also contours the donor area, leading to an overall improved silhouette.
Hand Rejuvenation
Fat grafting is also effective for hand rejuvenation. As people age, their hands can lose volume, leading to visible veins and tendons. Injecting fat into the hands can restore lost fullness and improve skin texture.
This application is less known but equally important. Patients report feeling more confident with youthful-looking hands. The procedure mirrors those used in facial applications, making it quite versatile.
Role of Adipose Stem Cells
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
Adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) are found in harvested fat. These stem cells are a type of mesenchymal stem cell. They have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including adipocytes. ASCs play a crucial role in fat grafting techniques. They enhance the regenerative properties of adipose tissue.
ASCs contribute significantly to tissue regeneration. They release growth factors that promote healing. These growth factors improve blood flow and stimulate new tissue formation. This process is essential for adipocyte graft survival. The presence of ASCs in grafts can lead to better integration with surrounding tissues.
Enhancing Graft Survival
Graft survival is a major concern in fat grafting procedures. Many factors affect how well the graft takes. The viability of the adipocytes is critical. ASCs help maintain this viability by supporting cellular functions. They also reduce inflammation around the graft site.
Studies show that using ASCs can increase the success rate of fat grafts. Research has demonstrated that adding ASCs to grafts improves their longevity and effectiveness. In one study, researchers observed a significant increase in graft retention when ASCs were included. This indicates their potential in enhancing overall outcomes.
Therapeutic Applications
Ongoing research explores the therapeutic applications of ASCs in regenerative medicine. Scientists investigate their use in treating various conditions. These include wound healing, orthopedic injuries, and even heart disease. The regenerative properties of ASCs make them promising candidates for future therapies.
Researchers are particularly interested in how ASCs interact with other cell types. Understanding these interactions can lead to improved treatment strategies. For example, combining ASCs with bone marrow-derived stem cells may boost healing processes further.
Clinical trials are underway to assess the safety and efficacy of ASC treatments. Early results indicate positive outcomes for patients receiving ASC-based therapies. These findings could revolutionize how we approach regenerative medicine.
Scientific Principles and Innovations
Cell Viability
Fat cell viability is crucial for successful fat grafting. These cells must survive the transfer process to function effectively. Gentle handling during extraction and injection helps maintain their health. Trauma can lead to cell death, reducing the effectiveness of the graft. Studies show that over 50% of fat cells can die if not treated properly.
Maintaining appropriate temperatures during procedures also affects cell survival. Cold conditions can harm fat cells, while warmth encourages their stability. Medical professionals emphasize these principles in training and practice.
Recent Innovations
Innovations like nanofat and microfat grafting have emerged in recent years. Nanofat grafting involves processing fat into smaller particles. This technique allows for better integration into tissues. It is particularly effective for delicate areas, such as the face.
Microfat grafting uses slightly larger fat particles. This method provides volume while maintaining a natural appearance. Both techniques enhance aesthetic results and reduce complications.
Clinical trials in the 1990s laid the groundwork for these advancements. Researchers explored various methods to improve fat grafting outcomes. Today, many practitioners adopt these innovations to refine their techniques.
Imaging Technologies
Imaging technologies play a vital role in planning fat grafting procedures. Techniques like ultrasound and 3D imaging help surgeons assess the treatment area. These tools allow for precise measurements and better visualization of anatomy.
Surgeons can identify specific volumes needed for optimal results. They can also monitor tissue response post-procedure using imaging technology. This ongoing assessment helps ensure that grafted fat integrates well with surrounding tissues.
These advancements contribute significantly to patient satisfaction and safety. Enhanced planning leads to more predictable outcomes, minimizing risks associated with fat grafting.
Postoperative Care and Anesthesia
Recovery Process
Swelling and bruising are common after fat grafting surgery. Patients can expect these symptoms to last for several days. The degree of swelling varies based on the individual and the extent of the procedure. Most people experience noticeable changes within the first week.
Downtime is essential for recovery. Patients should plan to take at least a week off from work or regular activities. Light exercise can usually resume after two weeks. Full recovery may take several months, depending on how the body heals.
Importance of Care Instructions
Following postoperative care instructions is crucial for optimal results. Plastic surgeons provide detailed guidelines on how to care for the surgical site. Ignoring these instructions can lead to complications, such as infection or poor healing.
Patients must keep the area clean and dry. They should avoid strenuous activities that could strain the body. Keeping follow-up appointments with the plastic surgeon is also important. These appointments help monitor healing and address any concerns.
Types of Anesthesia
Anesthesia plays a key role in fat grafting procedures. The type used depends on the surgery’s extent and patient needs. Local anesthesia numbs only the specific area being treated. This option is suitable for smaller procedures with minimal discomfort.
IV anesthesia provides deeper sedation while allowing patients to remain responsive. This method is often chosen for more extensive surgeries. General anesthesia may be necessary for large-scale fat grafting, where patients need to be fully unconscious.
Surgeons evaluate each patient’s health before deciding on anesthesia types. They consider factors like medical history and anxiety levels. Discussing options with a plastic surgeon helps ensure comfort during surgery.
Potential Complications
Complications can arise from fat grafting procedures. Common issues include infections, excessive bleeding, or unfavorable scarring. Patients should be aware of signs that indicate complications, such as increased pain or unusual discharge.
Seeking immediate medical attention for any concerning symptoms is vital. Early intervention can prevent more serious problems later on.
Final Remarks
Fat grafting is a powerful technique that can enhance your body’s natural beauty. You’ve learned about the various methods for harvesting and processing fat, along with the vital role of adipose stem cells. Understanding these techniques helps you make informed decisions for your cosmetic goals.
As you consider fat grafting, think about the benefits it offers, like improved contours and rejuvenated skin. Always choose a qualified professional to ensure safety and effectiveness. Your journey to achieving your desired look starts with knowledge and preparation. Ready to explore fat grafting further? Reach out to a specialist today and take the next step toward transforming your aesthetic vision into reality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is fat grafting?
Fat grafting is a cosmetic procedure that transfers fat from one part of the body to another. It enhances volume and contours, making it popular for facial rejuvenation and body sculpting.
How is fat harvested for grafting?
Fat is harvested using liposuction techniques. Common methods include tumescent liposuction and power-assisted liposuction, which ensure minimal trauma and better fat viability.
What processing methods are used in fat grafting?
Processing methods include decanting, centrifugation, and filtration. These techniques help isolate viable fat cells, removing impurities and ensuring higher survival rates after transplantation.
Where can fat be injected during grafting?
Common areas for fat grafting include the face, breasts, buttocks, and hands. Each area benefits from enhanced volume and improved aesthetic appearance.
What role do adipose stem cells play in fat grafting during a liposuction procedure in plastic surgery, especially around the hips and minimizing scars?
Adipose stem cells promote healing and tissue regeneration. They enhance the longevity of the grafted fat and improve overall outcomes by stimulating surrounding tissues.
What should I expect during postoperative care?
Postoperative care includes monitoring swelling, avoiding strenuous activities, and following your surgeon’s instructions. Proper care ensures optimal results and minimizes complications.
What type of anesthesia is used in fat grafting?
Fat grafting typically uses local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia, depending on the extent of the procedure. Your surgeon will recommend the best option for your needs.

 /
/ 